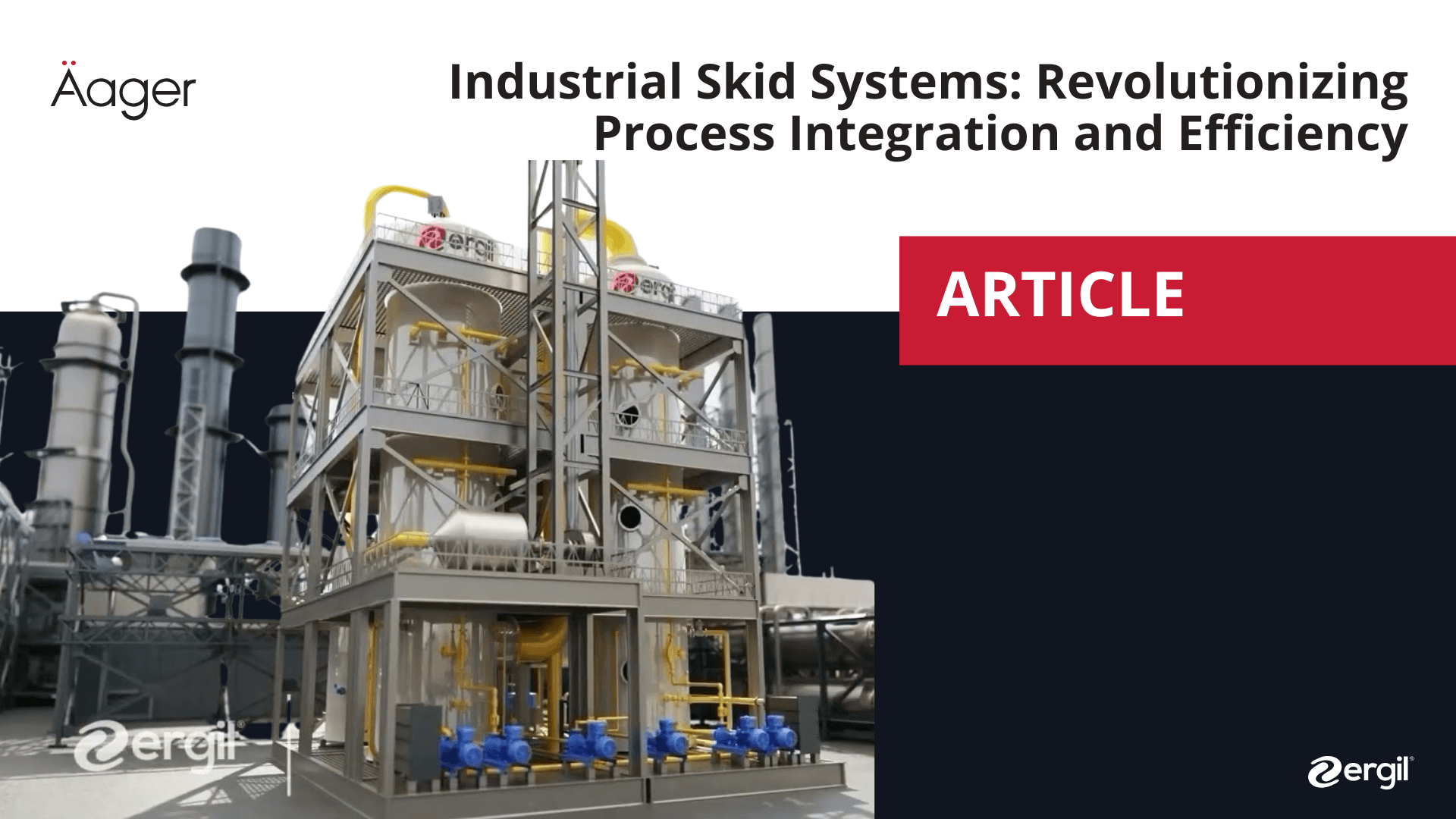
Industrial Skid Systems: Revolutionizing Process Integration and Efficiency
Industrial skid systems have become integral to modern manufacturing and processing operations across various industries. These pre-fabricated, self-contained units offer a compact, efficient, and cost-effective solution for a wide range of industrial processes. From oil and gas to pharmaceuticals, skid systems are transforming the way companies approach equipment installation and process integration.
What Are Industrial Skid Systems?
Industrial skid systems, also known as skid-mounted systems or process skids, are modular units that integrate various components of a process system onto a single frame or base. These systems typically include pumps, valves, instrumentation, piping, and control systems, all pre-assembled and mounted on a structural steel frame or "skid."
The concept of skid systems originated in the oil and gas industry but has since expanded to numerous other sectors, including:
- Chemical processing
- Water treatment
- Food and beverage production
- Pharmaceutical manufacturing
- Power generation
- Biofuel production
Key Benefits of Skid Systems
- Reduced On-Site Installation Time: Skid systems arrive pre-assembled, significantly reducing installation time and associated labor costs.
- Quality Control: Factory assembly allows for better quality control and testing before delivery to the site.
- Space Efficiency: Compact design optimizes floor space in manufacturing facilities.
- Mobility: Skid-mounted systems can be easily relocated if process requirements change.
- Standardization: Repeatable designs lead to consistent performance across multiple installations.
- Reduced Engineering Costs: Pre-engineered solutions minimize custom design requirements.
- Faster Project Completion: Parallel construction of skids and site preparation accelerates project timelines.
Types of Industrial Skid Systems
- Pump Skids: Integrating pumps, motors, and associated controls for fluid transfer applications.
- Filtration Skids: Incorporating various filtration technologies for liquid or gas purification.
- Heat Exchanger Skids: Combining heat exchangers with pumps and controls for thermal management.
- Metering Skids: Precision measurement and control of fluid flow rates in process streams.
- Chemical Injection Skids: Accurate dosing of chemicals into process streams.
- Compressor Skids: Packaged air or gas compression systems for industrial applications.
- Steam Generation Skids: Compact boiler systems for on-demand steam production.
- Water Treatment Skids: Modular systems for water purification and wastewater treatment.
Skid System Manufacturing Process
The production of industrial skid systems involves several key steps:
- Design and Engineering:
- 3D modeling and simulation of the skid layout
- Component selection and integration planning
- Structural analysis of the skid frame
- Fabrication:
- Cutting and welding of the structural steel frame
- Installation of major equipment components
- Piping fabrication and installation
- Electrical and Instrumentation:
- Wiring of electrical systems
- Installation of control panels and instrumentation
- Integration of automation and control systems
- Testing and Quality Assurance:
- Hydrostatic testing of piping systems
- Functional testing of individual components
- Integrated system testing and performance verification
- Surface Treatment and Painting:
- Sandblasting or chemical cleaning of surfaces
- Application of primer and finish coats
- Specialized coatings for corrosive environments
- Documentation and Certification:
- Preparation of operation and maintenance manuals
- Compilation of material certificates and test reports
- Acquisition of relevant certifications (e.g., ASME, CE marking)
Critical Considerations When Purchasing Skid Systems
- Process Requirements:
- Clearly define flow rates, pressures, temperatures, and other critical parameters
- Consider future capacity needs and potential process changes
- Site Conditions:
- Evaluate available space and access for installation
- Consider environmental factors (temperature, humidity, corrosive atmospheres)
- Assess utility availability (power, water, compressed air)
- Regulatory Compliance:
- Ensure the skid system meets all relevant industry standards and regulations
- Verify compliance with local codes and permitting requirements
- Material Selection:
- Choose materials compatible with process fluids and operating conditions
- Consider corrosion resistance and longevity of components
- Control System Integration:
- Determine the level of automation required
- Ensure compatibility with existing plant control systems
- Maintenance Accessibility:
- Verify ease of access for routine maintenance and component replacement
- Consider the availability of spare parts and local service support
- Transportation and Installation:
- Plan for logistics of transporting the skid to the installation site
- Assess lifting and positioning requirements at the site
- Vendor Expertise and Support:
- Evaluate the manufacturer's experience in your specific industry
- Consider the level of after-sales support and training offered
- Total Cost of Ownership:
- Look beyond initial purchase price to consider long-term operational costs
- Factor in energy efficiency and maintenance requirements
- Customization vs. Standardization:
- Determine if a standard skid design can meet your needs or if customization is necessary
- Balance the benefits of customization against potential cost and lead time implications
Case Study: Ergil's Approach to Skid System Manufacturing
Ergil, a leading manufacturer of industrial equipment, exemplifies best practices in skid system production. Their approach includes:
- Modular Design Philosophy: Ergil's skid systems are designed with modularity in mind, allowing for easy expansion and modification as process needs evolve.
- Advanced 3D Modeling: Utilizing state-of-the-art CAD software, Ergil creates detailed 3D models of skid systems, enabling virtual walk-throughs and clash detection before fabrication begins.
- In-House Testing Facilities: Comprehensive testing capabilities ensure that each skid system meets or exceeds performance specifications before shipment.
- Global Compliance: Ergil's skid systems are designed to meet international standards, facilitating deployment in various global markets.
- Industry-Specific Expertise: With experience across multiple sectors, Ergil tailors skid designs to the unique requirements of each industry, from oil and gas to water treatment.
Future Trends in Industrial Skid Systems
- IoT Integration: Incorporation of sensors and connectivity for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance.
- Modular Scalability: Design approaches that allow for easier capacity expansion through the addition of interconnected skid modules.
- Energy Efficiency: Greater focus on optimizing energy consumption within skid systems through advanced controls and high-efficiency components.
- Additive Manufacturing: Exploration of 3D printing technologies for producing complex components and reducing lead times.
- Augmented Reality Support: Implementation of AR technologies for remote troubleshooting and maintenance guidance.
Industrial skid systems represent a significant advancement in process equipment integration, offering numerous benefits in terms of efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness. As industries continue to evolve, skid systems are likely to play an increasingly important role in streamlining operations and enhancing productivity.
When considering the purchase of a skid system, careful evaluation of process requirements, site conditions, and long-term operational factors is essential. By partnering with experienced manufacturers and leveraging the latest technologies, companies can maximize the benefits of skid-mounted solutions and position themselves for success in an increasingly competitive industrial landscape.