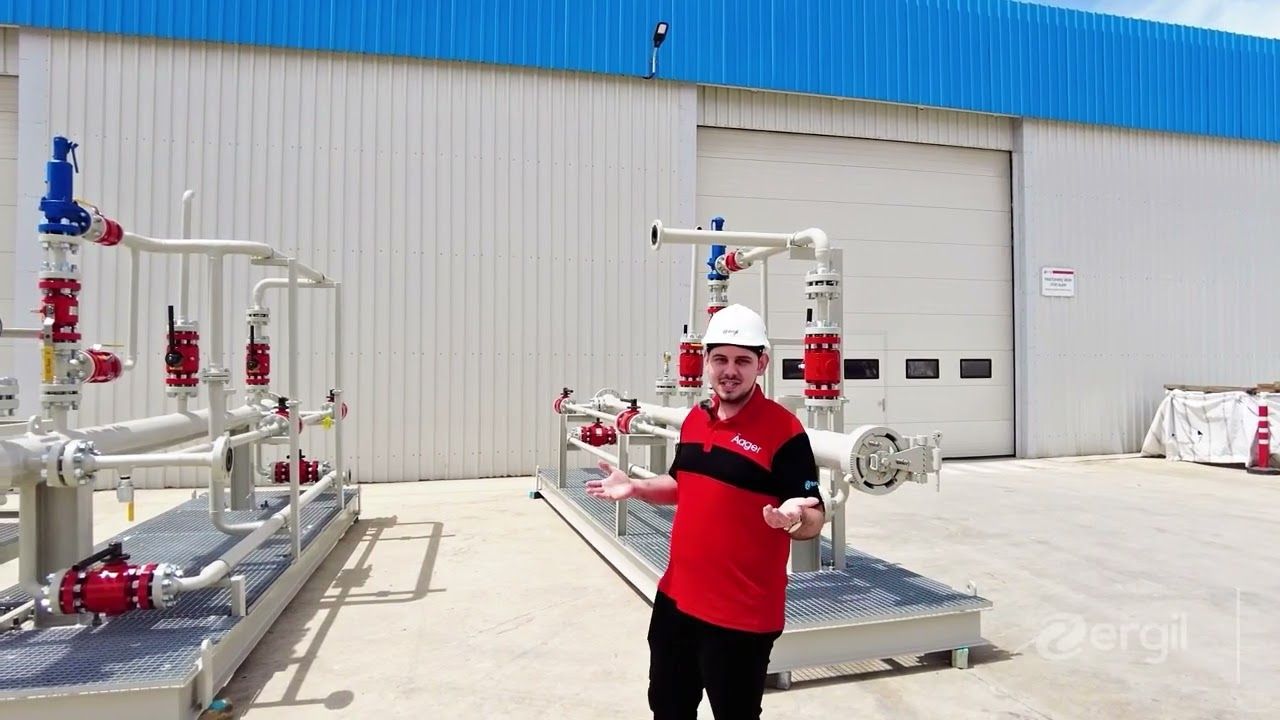
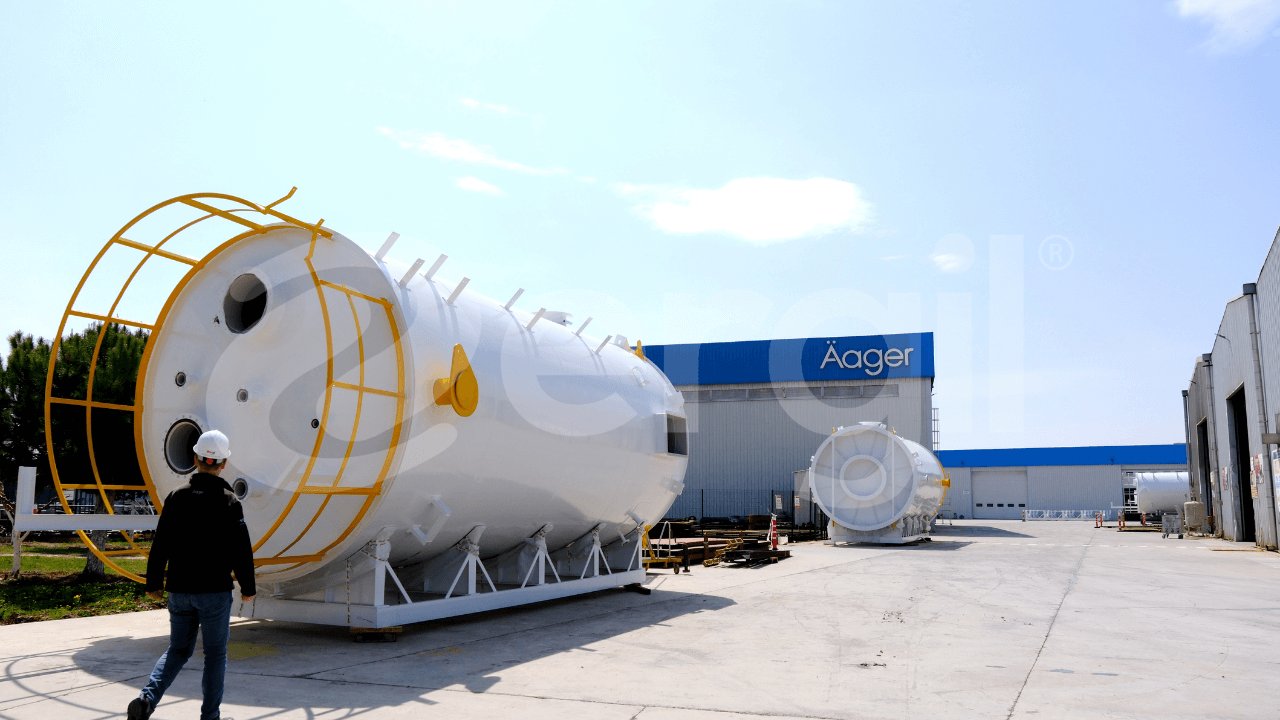
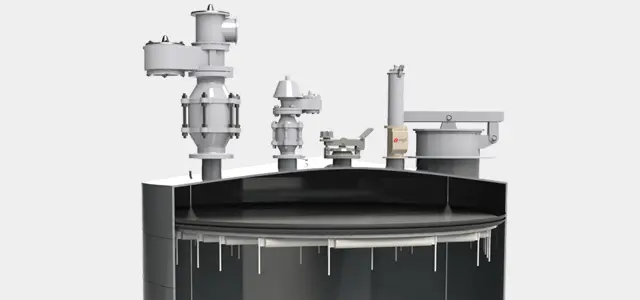
What are the application areas of wet packed scrubbers?
Wet packed scrubbers are used in various industries and applications due to their efficiency in removing pollutants from gas streams. Some of the key application areas include:
Chemical Manufacturing: In chemical plants, wet scrubbers are used to remove harmful chemicals, gases, and particulates that are by-products of chemical reactions and processing.

Key Applications in Chemical Manufacturing
- Control of Hazardous Emissions: Chemical plants produce a variety of emissions, including volatile organic compounds (VOCs), acidic and basic gases, particulate matter, and toxic fumes. Wet scrubbers are employed to remove these contaminants from exhaust gases before they are released into the atmosphere.
- Process-Specific Applications:
- Reactors and Synthesis Processes: During chemical reactions, especially those involving chlorination, sulfonation, nitration, or polymerization, harmful gases like hydrogen chloride, sulfur dioxide, and nitrogen oxides can be released. Wet scrubbers neutralize these gases, converting them into less harmful substances.
- Solvent Recovery and Handling: In processes where organic solvents are used, scrubbers capture solvent vapors, reducing VOC emissions and facilitating solvent recovery for reuse.
- Waste Treatment and Disposal: In the treatment of chemical waste, scrubbers control emissions of hazardous gases generated during waste processing.
How Wet Packed Scrubbers Work in Chemical Manufacturing
- Absorption and Neutralization:
Wet scrubbers use a liquid, often water or a chemically active solution, to absorb and neutralize gaseous pollutants. The contaminated gas stream is passed through a packed bed or spray tower where it contacts the scrubbing liquid.
Acidic gases like hydrogen chloride are neutralized by alkaline scrubbing solutions, while basic gases are treated with acidic solutions, resulting in the formation of neutral salts and water.
- Particulate Removal:
Apart from gases, scrubbers effectively remove particulates from exhaust streams. The liquid droplets in the scrubber capture and consolidate particulate matter, which is then collected and removed from the system.
- Gas-Liquid Contact Optimization:
The design of the scrubber, including the choice of packing material (ceramic, plastic, or metal), packing depth, and nozzle design, is tailored to maximize the gas-liquid contact area, ensuring efficient pollutant removal.
Benefits in Chemical Manufacturing
- High Efficiency in Pollutant Removal: Wet scrubbers can achieve high removal efficiencies for a wide range of pollutants, crucial in meeting stringent environmental regulations.
- Handling Corrosive and Toxic Gases: These systems are particularly effective in capturing and neutralizing corrosive and toxic gases, which are commonplace in chemical manufacturing.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: The design of wet scrubbers can be adapted to handle varying flow rates, temperature, and pollutant loadings, making them suitable for different processes within chemical plants.
Safety and Compliance: By reducing harmful emissions, wet scrubbers play a critical role in ensuring occupational safety and environmental compliance in chemical manufacturing facilities.
Power Generation: They are used in power plants, especially those burning fossil fuels, to remove sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter from flue gases.

Key Applications in Power Generation
- SO2 and NOx Emission Control: Power plants, especially coal and oil-fired ones, emit significant amounts of SO2 and NOx, which are major contributors to air pollution and acid rain. Wet scrubbers are used to remove these gases from the flue gas stream.
- Particulate Matter Removal: In addition to gaseous pollutants, combustion processes in power plants generate particulate matter. Wet scrubbers capture these particles, thereby reducing overall emissions.
- Mercury and Heavy Metal Control: Some wet scrubbers are also designed to capture mercury and other heavy metals present in the flue gas, further contributing to environmental protection.
How Wet Packed Scrubbers Work in Power Generation
- Flue Gas Desulfurization (FGD):
- In scrubbers designed for SO2 removal, typically limestone (CaCO3) or lime (Ca(OH)2) slurries are used. The SO2 in the flue gas reacts with the alkaline scrubbing solution to form calcium sulfate (gypsum), which can be commercially utilized.
- This process not only removes SO2 but also contributes to the generation of by-products that can be used in construction and agriculture.2. NOx Reduction:For NOx removal, scrubbers may use solutions that selectively reduce NOx compounds into nitrogen and water, employing reagents like ammonia or urea.3. Advanced Operational Mechanisms:Modern scrubbers in power plants are often equipped with advanced features like spray towers, packed beds, or fluidized beds to enhance the gas-liquid contact and improve pollutant removal efficiency.
Benefits in Power Generation
- High Removal Efficiencies: Wet scrubbers in power plants can achieve high removal rates for SO2, NOx, and particulates, essential for compliance with environmental regulations.
- By-Product Utilization: The by-products of scrubbing, like gypsum, can be commercially valuable, offsetting some operational costs.
- Flexibility and Compatibility: Wet scrubbers can be retrofitted into existing power plants and designed to accommodate varying capacities and emission requirements.
- Contribution to Environmental Protection: By significantly reducing harmful emissions, these systems play a vital role in protecting air quality and public health.
Metal Processing: In the metal processing industry, wet scrubbers help in removing particulates and gases (Dichloromethane, Toluen, Benzene, etc.) generated during smelting and other metalworking processes.
Mining and Mineral Processing: They are employed in mining operations to control dust and harmful gases released during the extraction and processing of minerals.
Waste Incineration: Wet scrubbers are used in waste incineration facilities to remove acidic gases (SO2, CO2, NO2 etc.) and particulates from the combustion of municipal and industrial waste.
Pharmaceutical Industry: They are used to control emissions of particulates and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) generated during drug manufacturing processes.

Key Applications in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
- Emission Control During Drug Production: During various stages of pharmaceutical production, including synthesis, mixing, and packaging, harmful emissions such as VOCs, solvent vapors, and particulate matter are generated. Wet scrubbers are used to remove these pollutants from the exhaust stream.
- Control of Biological and Chemical Hazards: Pharmaceutical processes often involve the use of potent, active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and other bioactive compounds. Wet scrubbers help in controlling emissions of these substances, ensuring a safe work environment and preventing environmental contamination.
- Odor Management: In addition to pollutant removal, scrubbers are effective in controlling odors that may arise from certain pharmaceutical processes, contributing to workplace comfort and adherence to environmental standards.
Functionality of Wet Packed Scrubbers in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
- Chemical Absorption and Neutralization:
-
- Wet scrubbers in the pharmaceutical industry often use chemical reagents to neutralize or absorb specific pollutants. For instance, acidic or basic solutions can be used depending on the nature of the emissions.
- The design of the scrubber, including packing material and the configuration of the spray system, is optimized for maximum contact between the polluted air stream and the scrubbing liquid.
- Particulate Removal:These systems effectively capture particulates, including fine powders that are common in pharmaceutical manufacturing, by trapping them in liquid droplets within the scrubber system.
- Solvent Recovery:In certain configurations, wet scrubbers can facilitate the recovery of valuable solvents from the exhaust stream, which can then be reused in the manufacturing process.
Benefits in the Pharmaceutical Industry
- High Removal Efficiencies: Pharmaceutical processes demand high levels of pollutant removal efficiency, which wet scrubbers can reliably provide.
- Customizable Systems: The design of wet scrubbers can be customized to target specific pollutants typical in pharmaceutical manufacturing, ensuring compliance with stringent industry standards.
- Enhanced Safety and Compliance: By controlling harmful emissions, these systems play a critical role in ensuring the safety of the work environment and helping pharmaceutical facilities comply with environmental and health regulations.
Economic Advantages: The ability to recover solvents and other valuable compounds from the exhaust stream can provide economic benefits to pharmaceutical companies.
Food Processing: In this industry, they help in removing odors (H2S, NH3, VOC etc.) and particulate matter generated during various food processing activities.

Role of Wet Packed Scrubbers in Food Processing
- Odor Control: One of the primary uses of wet scrubbers in food processing is to manage odors emanating from cooking, baking, fermentation, and other processing activities. These odors, if not controlled, can affect product quality and workplace environment.
- Particulate and VOC Removal: Various stages of food processing, such as grinding, mixing, and cooking, can release particulates and VOCs. Wet scrubbers capture these emissions, ensuring compliance with air quality standards.
- Emissions from Preservation Processes: In processes like smoking or curing, wet scrubbers are used to control the emissions of smoke and other preservation-related compounds.
Operational Aspects of Wet Packed Scrubbers in Food Processing
- Mechanism of Action:
- Wet scrubbers in the food industry often utilize water or chemically treated solutions to absorb and neutralize airborne pollutants and odors.
- The exhaust gases are passed through a packed bed or mist of the scrubbing liquid, where pollutants are trapped and neutralized.
- Design Considerations:The choice of packing material, scrubber design, and the specific chemical composition of the scrubbing liquid are tailored to target the specific types of emissions prevalent in food processing.
Advantages in the Food Processing Industry
- Effective Emission Control: Wet scrubbers offer high efficiencies in removing odors, particulates, and VOCs, essential for maintaining product quality and a safe working environment.
- Customization for Specific Needs: The design and operation of these systems can be customized to suit different types of food processing activities, offering flexibility and targeted control.
- Compliance with Regulations: By reducing emissions, these systems help food processing plants comply with environmental and health regulations, preventing community complaints and potential legal issues.
Enhanced Workplace Environment: Controlling emissions and odors contributes to a more pleasant and healthier workplace, which is crucial in the food industry.
Pulp and Paper Industry: Wet scrubbers are used to control emissions of sulfur compounds (SO2, H2S, MDI, TDI, Odor etc.) and particulates from paper manufacturing processes.
Applications of Wet Packed Scrubbers in Pulp and Paper Manufacturing
- Sulfur Compound Emission Control: Pulp and paper production often involves processes that release sulfur compounds, such as sulfur dioxide (SO2) and hydrogen sulfide (H2S). Wet scrubbers are used to remove these compounds from the exhaust gases.
- Particulate Matter Removal: These systems are also effective in capturing particulates produced during various stages of paper manufacturing, including wood processing, pulping, and paper finishing.
- Odor Management: The pulp and paper industry is known for generating odorous gases. Wet scrubbers play a vital role in controlling these odors, thus reducing nuisances to surrounding communities and improving workplace conditions.
Operational Mechanism in Pulp and Paper Industry
- Chemical Absorption and Neutralization:
-
- Wet scrubbers in this industry typically use alkaline reagents to neutralize acidic gases like SO2, transforming them into less harmful by-products.
- The exhaust gases are passed through a packed tower or spray chamber where they come into contact with the scrubbing liquid, facilitating the absorption and neutralization process.
- Particulate Capture:The scrubbing liquid captures particulates present in the exhaust stream, consolidating them into larger droplets which are then removed from the system.
- Design and Material Considerations:The design, including the choice of packing material and configuration, is optimized for maximum efficiency in gas-liquid contact, ensuring effective pollutant removal.
Benefits in the Pulp and Paper Industry
- High Removal Efficiencies: These systems offer high efficiencies in removing sulfur compounds and particulates, crucial for meeting environmental regulations and reducing air pollution.
- Adaptability and Customization: Wet scrubbers can be tailored to the specific needs of a pulp and paper facility, accommodating various process emissions and flow rates.
- Enhanced Environmental Compliance: By controlling harmful emissions, wet scrubbers ensure that pulp and paper plants adhere to stringent environmental standards.
- Improved Workplace and Community Health: Effective control of odors and pollutants contributes to a safer and more pleasant working environment, as well as minimizes impact on nearby communities.
Agricultural Facilities: They are employed in controlling dust and odor emissions (H2S, NH3, VOC etc.) from livestock rearing and processing facilities.
Application of Wet Packed Scrubbers in Agriculture
- Livestock Odor and Emission Control: Agricultural facilities, especially large-scale livestock operations, generate significant amounts of odors and gaseous emissions. Wet scrubbers are used to treat the air from barns, manure storage, and processing areas to control these emissions.
- Dust Reduction in Processing Plants: Agricultural processing plants, such as those for grain or feed, produce considerable amounts of particulate matter. Wet scrubbers capture this dust, thereby improving air quality and reducing potential health hazards.
- Greenhouse Gas Mitigation: Some agricultural processes release greenhouse gases like methane and nitrous oxide. Wet scrubbers can be equipped to mitigate these emissions, contributing to climate change mitigation efforts.
Operational Mechanics in Agricultural Facilities
- Absorption and Scrubbing Process:
The scrubbers use water or chemically treated solutions to absorb gases, odors, and particulates from the air exhausted from agricultural facilities.
The contaminated air passes through a packed bed or spray system where it comes into contact with the scrubbing liquid, facilitating pollutant removal.
- Design Considerations for Efficiency:
The design, including the selection of packing materials and the layout of the scrubbing system, is tailored to the specific types of emissions prevalent in agricultural operations.
Advantages in Agricultural Settings
- Effective Control of Odors and Particulates: Wet scrubbers offer high efficiencies in capturing odors and dust, essential for maintaining air quality standards in and around agricultural facilities.
- Customization for Specific Agricultural Needs: The systems can be designed to suit different types of agricultural activities, offering flexibility and targeted pollution control.
- Environmental Compliance and Community Relations: By reducing emissions, these systems help agricultural facilities comply with environmental regulations and maintain good relations with neighboring communities.
- Enhanced Worker and Animal Health: Effective control of emissions contributes to a healthier environment for both workers and animals within agricultural facilities.
Asphalt Production and Roofing: In these industries, scrubbers are used to control emissions of particulates and fumes.
Applications in Asphalt and Roofing
- Asphalt Production: Used to control emissions during the heating and mixing processes. They capture particulates and fumes, including VOCs, ensuring cleaner exhaust gases.
- Roofing Material Manufacturing: Scrubbers control fumes released during the production of roofing materials, such as shingles and tar paper, reducing the release of harmful compounds into the atmosphere.
Operational Dynamics
- Efficient Emission Control: Wet scrubbers in these industries are designed to effectively capture and neutralize a range of pollutants, including particulates and fumes, through absorption and chemical reactions.
- Customizable Systems: The scrubber systems are adaptable to handle the specific emission characteristics of asphalt production and roofing material manufacturing.
Glass Manufacturing: They help in controlling the emissions of particulate matter and gaseous pollutants from glass furnaces.
Application in Glass Manufacturing
- Controlling Particulate Emissions: The glass manufacturing process, particularly during melting and refining, generates significant amounts of fine particulates. Wet scrubbers capture these particles, reducing their release into the atmosphere.
- Managing Gaseous Pollutants: These systems also control various gaseous emissions, including sulfur dioxide (SO2) and other harmful gases produced during the melting of raw materials.
Operational Dynamics
- Efficient Removal of Pollutants: Wet scrubbers in glass manufacturing facilities are designed to effectively absorb and neutralize pollutants through direct contact with a scrubbing liquid.
- Customizable Design: The design of these systems can be tailored to handle the specific types and volumes of emissions characteristic of glass production processes.
Semiconductor Manufacturing: Wet scrubbers are used to remove toxic and corrosive gases produced during the production of semiconductors and electronic components.
Applications in Semiconductor Manufacturing
- Controlling Toxic Gas Emissions: Processes such as etching, cleaning, and doping in semiconductor manufacturing release various harmful gases like hydrogen fluoride, chlorine, and silane. Wet scrubbers are used to absorb and neutralize these gases.
- Particulate Matter Removal: The production of semiconductors also generates fine particulates, which wet scrubbers efficiently capture, preventing them from contaminating the workplace and the environment.
Operational Dynamics
- Efficient Gas Absorption: Wet scrubbers in semiconductor facilities are designed to maximize contact between the exhaust gases and the scrubbing liquid, facilitating effective absorption and neutralization of toxic gases.
- Design Adaptability: These systems are tailored to handle the unique chemical characteristics and concentrations of emissions typical in semiconductor production.
In each of these applications, the specific design and operation of the wet scrubber system can vary significantly depending on the characteristics of the emissions being controlled, including the type and concentration of pollutants and the volume of the gas stream.
For which chemicals wet packed scrubbers can be used?
Wet packed scrubbers are versatile in their application and can be used to remove a wide range of chemicals and pollutants from industrial gas streams. Some of the key chemicals and categories of pollutants that these scrubbers can effectively control include:
- Particulate Matter (PM): They are effective in capturing both fine and coarse particulate matter, including dust, metal fumes, and other solid particles.
Capture Mechanism:
The scrubbing liquid, usually water or a chemically treated solution, captures PM as the contaminated air passes through the scrubber.
The particles are trapped in the liquid droplets and then collected and removed from the exhaust stream.
Types of PM Controlled:
Combustible Dust: Such as wood, coal, and grain dust, which can be a fire hazard if not adequately controlled.
Non-Combustible Dust: Includes minerals, metal fumes, and other incombustible materials.
Bioaerosols: In industries like agriculture and food processing, bioaerosols such as spores and microorganisms can be controlled using wet scrubbers.
Design Considerations for PM Removal:
Packing Material and Depth: The choice of packing material and its depth in the scrubber impacts the efficiency of PM capture.
Liquid-to-Gas Ratio: An optimal liquid-to-gas ratio is crucial for effective particulate removal.
Droplet Size and Distribution: The size and distribution of droplets in the scrubber influence the capture efficiency for different sizes of particulate matter.
- Sulfur Compounds: Wet scrubbers are commonly used to remove sulfur compounds such as sulfur dioxide (SO2) and hydrogen sulfide (H2S), which are typical in fossil fuel combustion and refining processes.
Mechanism of Control for Sulfur Compounds
Chemical Absorption:
Wet scrubbers use a liquid solvent, typically water or an alkaline solution, to absorb sulfur compounds from the exhaust gas stream.
Alkaline scrubbing agents, like lime or limestone slurries, are commonly used to react with SO2, converting it into a less harmful by-product, such as calcium sulfate (gypsum).
Oxidation:
In some cases, scrubbing solutions facilitate the oxidation of H2S to sulfate, rendering it less harmful and odorous.
Physical Absorption:
For certain sulfur compounds, especially those that are less reactive, physical absorption using water or specific solvents can be effective.
- Nitrogen Oxides (NOx): They can be used to reduce NOx emissions from power plants and industrial combustion processes.
Chemical Absorption: This is the primary method for controlling sulfur compounds like sulfur dioxide (SO2) and hydrogen sulfide (H2S). The exhaust gas containing sulfur compounds is passed through a scrubber where it comes into contact with an alkaline scrubbing solution. Common scrubbing agents include lime (Ca(OH)2) or limestone (CaCO3) slurries.
For SO2: The SO2 in the gas reacts with the alkaline scrubbing solution to form calcium sulfite, which is then oxidized to form gypsum (calcium sulfate), a useful by-product in many industries.
For H2S: Similar to SO2, H2S can be absorbed and neutralized in an alkaline medium. The process often leads to the formation of elemental sulfur or sulfuric acid, depending on the oxidizing conditions within the scrubber.
Oxidation: Some wet scrubbers facilitate the oxidation of sulfur compounds. For example, H2S can be oxidized to sulfuric acid or sulfate salts in the presence of an oxidizing agent within the scrubbing solution.
Acidic Gases: These include hydrochloric acid (HCl), hydrofluoric acid (HF), and other acid gases generated in chemical processes and waste incineration.
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs): Wet scrubbers can be designed to remove VOCs, which are common in chemical, pharmaceutical, and petrochemical industries.
Mercury and Heavy Metals: Certain wet scrubber systems can effectively capture mercury vapors and other heavy metals emitted during industrial processes like metal smelting and coal combustion.
Chlorine and Chlorinated Compounds: These are common in the chemical industry and can be controlled using wet scrubbers.
Ammonia and Amine Compounds: Wet scrubbers can be used in fertilizer production and other industries where ammonia and amine compounds are prevalent.
Odorous Compounds: These include a variety of organic and inorganic compounds that cause odors, common in waste treatment and food processing industries.
Alcohols and Ketones: Used in various industrial manufacturing processes, these compounds can also be controlled with wet scrubbers.
The effectiveness of wet scrubbers in removing these pollutants depends on factors such as the design of the scrubber, the type of scrubbing liquid used, the contact time between the gas and the liquid, and the concentration and properties of the pollutants. Additionally, the selection of scrubbing liquid is crucial as it needs to react effectively with the specific pollutants present in the gas stream.
How does a scrubber work in the oil & gas industry?
In the oil and gas industry, scrubbers, particularly gas scrubbers, play a vital role in the processing and treatment of natural gas and in the management of emissions. The working principle of a scrubber in an oil field typically revolves around separating components from the natural gas stream and controlling pollution. Here’s a general overview of how they work:
Separating Components from Natural Gas
Removal of Liquids: In natural gas processing, scrubbers are often used to remove liquids such as water, oil condensates, and hydrocarbon liquids from the gas stream. This is crucial to prevent issues like pipeline corrosion and freezing.
- Operating Principle: The natural gas enters the scrubber where it encounters internals like baffles or a demister pad. These structures disrupt the flow, causing liquid droplets to coalesce and fall out of the gas due to gravity.
- Mist Extractors: Some scrubbers are equipped with mist extractors to remove very fine liquid droplets from the gas. These are especially important in high-pressure systems where tiny droplets can be carried with the gas.
Pollution Control
Removing Contaminants: Scrubbers in oil fields are also used to remove contaminants like hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and carbon dioxide (CO2) from the natural gas. These contaminants can be corrosive and are harmful to the environment.
- Absorption Process: The contaminated gas is passed through a liquid absorbent, typically an amine solution, which selectively absorbs the H2S and CO2. This process is commonly known as amine gas treating.
- Regeneration of Absorbent: After absorption, the absorbent is heated in a regenerator, which releases the captured H2S and CO2, allowing the absorbent to be reused.
Safety and Environmental Compliance
Emission Control: In addition to processing natural gas, scrubbers are also used to control emissions from other processes in oil fields, such as flaring or venting operations.
Compliance with Regulations: Scrubbers help in complying with environmental regulations by controlling the release of harmful pollutants into the atmosphere.
In summary, scrubbers in oil fields are essential for both processing natural gas (by removing liquids and contaminants) and for environmental protection (by controlling emissions of harmful gases). The specific design and operation of a scrubber in an oil field can vary depending on the composition of the natural gas, the type of contaminants present, and the regulatory requirements of the region.